Writing Complicated Tableau Calculations.
- Gowtham V

- Jun 26, 2022
- 2 min read
Writing calculated fields can be really difficult, especially when the logic is complex or there are multiple layers. In Tableau, I’ve come up with a handful of techniques that I’ve found make it easier to write complicated calculated fields, In this article I’m going to share those tips with you.
Before we get started, let’s define the scenario.
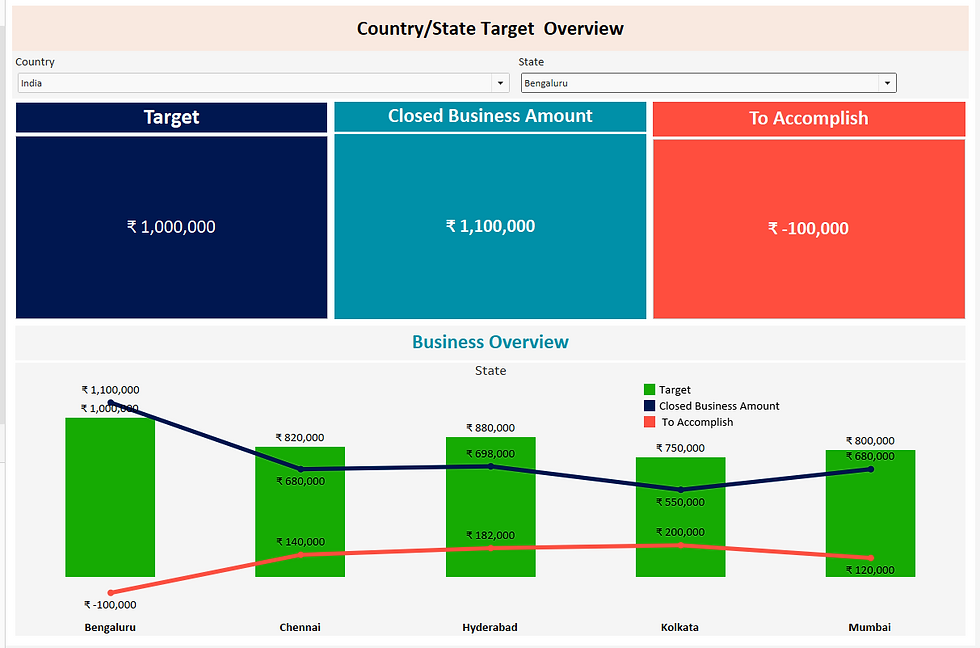
Scenario : We have Country and State attributes, Each country and associated states has a set of target and closed business amount. Based on the above available data we should build the following logic.
1. When Country is selected we should show country target and all the associated states, closed business amount. Difference of these two numbers will be shown in To Accomplish.
2. When State is selected we should show state target and the state closed business amount. Difference of these two number will be shown in To Accomplish.
* Scenario 1 Result

Scenario 2 Result
While Building the logics we should follow the below mentioned points.
* Break Logic Into Pieces
* Number Your Calculations
* Build A Table
* Comment Your Calculations.
To build the above scenario I have build the following formulas and logics.
1. Country Count
{ FIXED [Country] : COUNTD([State])}
2. State Count
COUNTD([State])
3. Total Target Country
ROUND(SUM({FIXED [State] :
max ([Target]
)}),1) ///Total Target
4. Country + State Target
IF SUM([1. Country Count])=[State Count]
THEN ZN([Total Target Country]) ///if country is equal to state
ELSEIF
SUM([1. Country Count]) <> [State Count] THEN
ZN([Country Target]) //// If country is not equal to state
END
5. Numbers Ranking
IF INT([4. Country + State Target]) = 0 then
1 ELSE INT([4. Country + State Target]) END ///If there is zero value it should covert to 1
6. Rank Unique - Target
RANK_UNIQUE([Numbers Ranking],"Desc") ///To filter the selected country & state value.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To Accomplish Formulas.
7. To Accomplish
[Target] - [Closed Business Amount]///Difference Amount
8. Cheat Formula
([4. Country + State Target])*([All State Closed Business])////To get the highest Number By Multiplying the target and all state closed business
9. Cheat Sheet Remove Zeros
IF [8. Cheat Sheet] = 0 or ISNULL([8. Cheat Sheet]) THEN 1 ELSE [8. Cheat Sheet] END
10.Rank Unique To Accomplish
RANK_UNIQUE([Cheat Sheet Removed Zeros],"Desc")
Step 11. From the rank unique to accomplish attribute filter 1st rank and make it as default filter.
Cross Tab Data.

Wrap-Up
So those are my four tips for writing complicated calculated fields. The examples I shared here are quite complex—they use advanced features like table calculations and data densification—but the techniques I’ve shared are applicable to anything that you consider complicated. By using these tips, I’m confident that you’ll be able to tackle tricky calculated fields like a pro.




Comments